Vitamin B1, also known as Thiamine, is a crucial mineral that is required by the body to process carbohydrates and provide energy. This vitamin also helps to maintain the proper functioning of the central nervous system.
Some factors that can lead to a deficiency of Vitamin B1 include over-dieting, excessive drinking, liver disorders, and kidney dialysis. People who consume a lot of processed foods, sweets, and soft drinks are also at a high risk of Vitamin B1 deficiency. Long-term alcohol consumption can reduce the absorption of this vitamin, along with other essential nutrients.
The consumption of thiamine-rich foods has several health benefits. It helps to maintain normal heart function, normalize carbohydrate metabolism, support normal nervous system functioning, and promote proper cyclic function.
Deficiency of Vitamin B1 can lead to symptoms like fatigue, irritability, poor memory, poor sleep, loss of appetite, and upset stomach. Supplementation of Vitamin B1 and treatment of the underlying cause is necessary to cure the deficiency.
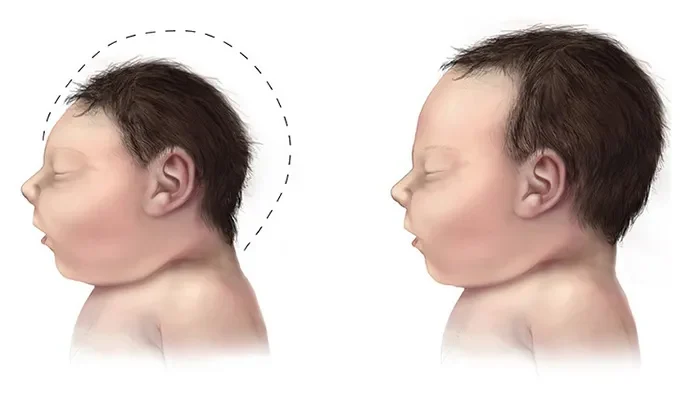
Breakfast cereals are an excellent source of Vitamin B1 and other essential vitamins. These cereals are often fortified with this nutrient, helping to maintain normal levels of Vitamin B1 in the body. Beriberi disease, caused by Vitamin B1 deficiency, has three forms – wet, dry, and cerebral.
Symptoms of low vitamin B1 or beriberi disease?
Wet Beriberi is associated with cardiovascular disease and symptoms may include swelling, increased heart rate, phlegm in the lungs, and heart shape change. Dry Beriberi and Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome are both associated with nervous system diseases and symptoms may include pain, tingling, loss of sensation in the hands and feet, muscle wasting, and paralysis.
Excessive alcohol consumption is a common cause of all three forms of Beriberi and can lead to fatal conditions such as brain damage and death. It is important to consume a balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals to maintain proper health and prevent deficiencies. Fortified breakfast cereals and natural foods like grains, corn, and oats are excellent sources of Vitamin B1 and other essential vitamins.
When Should a Doctor be Consulted?
If a person is experiencing symptoms related to beriberi, they should see a doctor and get a blood test done to confirm the issue.
Individuals with low Vitamin B1 levels should have regular blood tests to monitor their Vitamin B1 levels and determine the effectiveness of the treatment for beriberi and if their Vitamin B1 levels are improving.
Causes of Vitamin B1 deficiency (Beriberi)
Beriberi disease or Vitamin B1 deficiency is caused by several reasons, including:
- Consuming small amounts of vitamin B1-rich foods
- A diet that is deficient in Thiamine or Vitamin B1, including:
- Consuming mostly foods that contain milled rice, plain, and fresh water fish and shellfish
- Foods high in anti-thiamine factors such as tea, coffee, and beetle nuts
- Processed foods that destroy thiamine
There are also several dietary factors that reduce the consumption of Vitamin B1, including:
- Alcohol addiction
- Starvation
- Gastric bypass surgery with restricted calorie intake during recovery period
Increased metabolic consumption of Thiamine may result from:
- Consuming foods high in carbohydrates or saturated fat
- Pregnancy
- Hyperthyroidism
- Breastfeeding
- Fever
- Increased physical activity
There can also be a sudden decrease in Vitamin B1 levels due to:
- Diarrhea
- Diuretic drug therapy for high blood pressure
- Dialysis therapy
- Hyperemesis gravidarum (a severe form of morning sickness)
- Genetic disorders
In severe cases, beriberi can also be caused by an inherited disorder that prevents the absorption of Vitamin B1 from food.
How to prevent vitamin B1 deficiency or beriberi disease?

To prevent beriberi, it is important to consume sufficient amounts of foods high in Vitamin B1. Beriberi is rare as most people get enough Vitamin B1 from their diet. However, people in certain groups who are at higher risk of beriberi can prevent it by having regular blood tests to check their Vitamin B1 levels.
What food has the most vitamin B1?
Food sources of thiamine include:
- Milk
- Nuts (cashews, almonds, etc.)
- Oats
- Oranges
- Eggs
- Seeds
- Legumes
- Peas
- Yeast
- Brussels sprouts
- Spinach
- Beet green leaves
There are also some foods that contain vitamin B1 as a separate ingredient, including:
- Rice
- Bread
- Breakfast cereal
- Flour
How is Beriberi diagnosed?
Doctors may suspect a vitamin B1 deficiency in people who have already experienced symptoms related to beriberi, as well as the following factors:
- Chronic excessive alcohol consumption
- A special diet
- Malnutrition
Doctors perform a special test to check for:
- Lack of coordination between body parts
- Difficulty walking
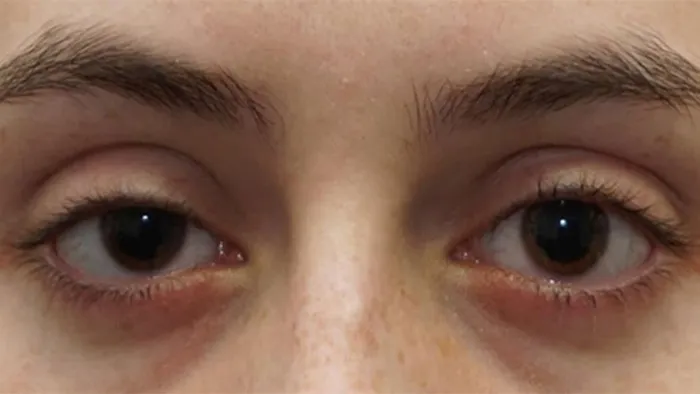
- Drooping eyelids
- Inactivity of bones and muscles in response to a stimulus
With a physical examination, doctors can also detect any heart-related problems, such as:
- Heart palpitations
- Leg swelling
- Drooping eyelids
- Breathing problems
You may need to undergo several tests to determine if you have beriberi.
With the help of a blood test and urine test, the amount of Vitamin B1 in the body can be checked. If your body is having difficulty absorbing vitamin B1, you will have low levels of vitamin B1 in your blood and high levels in your urine.
An echo test (echocardiogram) is done to check for heart failure, and MRI and CT scans are done to detect any mental changes in beriberi disease.
How do you fix B1 deficiency?
When there is a deficiency of more than one type of vitamin in the body, special monitoring is required as soon as treatment is started.
Medicines:
The main ways to reduce the possible symptoms and problems caused by beriberi are:
- Heart medications: If beriberi is diagnosed as wet beriberi and the patient has had the condition for a long time, heart functions may be affected, and heart medicines such as Digoxin, in addition to Vitamin B1, are required.
- Pain relievers: Depending on the severity of the neurological symptoms, pain relievers can relieve pain in the hands and feet due to neuropathy
- Other Vitamins – Based on the results of blood tests, the doctor may advise the patient to take supplements of other vitamins, which are available in tablet form. This treatment is often prescribed for individuals whose diets are lacking in several nutrients and who need medication to obtain additional vitamins.
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) – Depending on the symptoms of beriberi, the doctor may recommend vitamin B1 in tablet form, intravenously, or a combination of both. For mild deficiencies, a daily dose of 25 to 100 mg is prescribed, while for severe deficiencies, a dosage of 200 to 300 mg is recommended. If the deficiency is chronic, oral supplementation of vitamin B1 is advised.
Diseases caused by deficiency of Vitamin B1?
Beriberi can cause heart failure, which can be life-threatening if left untreated. Vitamin B1 deficiency may also be accompanied by deficiencies of other B-group vitamins, requiring additional treatment. In advanced stages of beriberi, individuals may experience memory loss, confusion, and other problems.
How much Vitamin B1 should be taken daily?
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin B1 (thiamine) varies depending on several factors such as age, sex, and pregnancy status. Generally, adult males need about 1.2-1.5 milligrams per day, while adult females need about 1.1-1.2 milligrams per day. During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the recommended daily intake may be higher.